What is Astaxanthin?
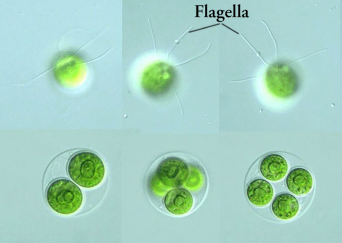
Haematococcus pluvialis algae cells become red as they accumulate the antioxidant carotenoid Astaxanthin.
Astaxanthin is so protective the cells can live for over 40 years without food or water and in extreme heat or cold.
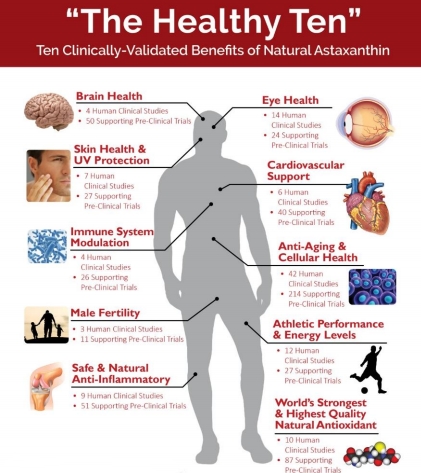
Natural Astaxanthin Health Benefits—The Healthy Ten
1) World’s Strongest & Highest Quality Natural Antioxidant
2) Safe & Natural Anti-Inflammatory
3) Eye Health
4) Brain Health
5) Beauty & Skin Health
6) Cardiovascular Health
7) Athletes & Energy
8) Immunity
9) Male Fertility
10) Anti-Aging & Cellular Health
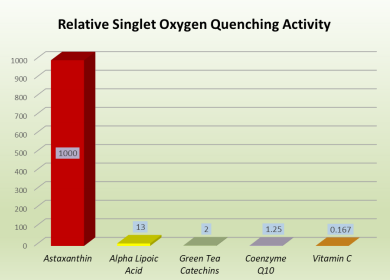
World’s Strongest Natural Antioxidant
*Singlet Oxygen Quenching
*800 times stronger than CoQ10
*550 times stronger than Green Tea Catechins
*6000 times stronger than Vitamin C
*550 times stronger than Vitamin E
*11 times stronger than Beta Carotene
Major Differences from Artificial Astaxanthin
ØSource: Natural is extracted from algae while Artificial is synthesized from petrochemicals.
ØStrength: Natural is 20 – 90 times stronger as an antioxidant.
ØAnimal Trials Prove Superiority: Five different preclinical trials in a variety of animals prove superior efficacy for Natural Astaxanthin for various health benefits including survival rates, resistance to stress, protection of internal organs, growth rates and longevity.
Molecule Shape, Esterification and Synergy: Natural Astaxanthin molecule is shaped differently; is 95% esterified; and comes complexed with small amounts of other naturally-occurring carotenoids.
ØSafety: Natural has an extensive portfolio of human safety studies and over 15 years of commercial use; Artificial has never been tested in humans.
ØEfficacy: Natural has been clinically validated to have many diverse health benefits in approximately 100 human clinical trials; Artificial has never been shown to have any health benefits.
ØDosage: Should Artificial Astaxanthin ultimately be proven safe for long-range human consumption, dosage would have to be at least 20 times greater than Natural due to its inferior antioxidant profile.






